Heat treatment |
|
|
|
|
Our heat treatment includes: |
|
|
|
|
|
· Short-time gas nitriding · Gas-nitro carburization with subsequent oxidation · Long-time gas nitriding · Stress-relief annealing · Retrieval of materials · Any heat treatment procedure up to 750°C · 2 shaft furnaces |
|
|
|
|
Key facts:Usable space diameter max. 1200 mm (47.24 inch) Usable hanging max. 4300 mm (169.29 inch) Usable standing max. 4700 mm (185.04 inch) Temperature max. 750°C Heating power 360 kW Workpiece weight max. 6 t |
|
|
|
|
|
Made by IMC |
|
|
|
|
|
The highest application duration made possible by advanced technology |
|
|
|
|
|
A component’s lifecycle absolutely depends on the heat treatment it underwent. Heat treatment is of major importance in our extruder cylinder and screw-shaft production chain. |
|
|
|
|
Nitration: |
|
|
|
|
|
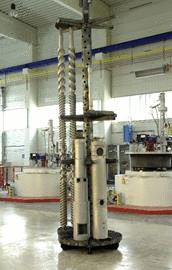
Screw-shafts or extruder cylinders to be treated are suspended or are put in an upright position in the vacuum-tight furnace during gas nitration and heated to a temperature of 530° Celsius. During heating or treatment time, which may last 40 to 120 hours, the pieces are exposed to nitrogen and ammonia. Narrow and inside contours are also nitrated and then become wear- and corrosion-resistant. |
|
|
|
|
|
IMC owns one of the most advanced nitration plants where parts up to 4,700 mm long with a max. diameter of 1,200 mm are horizontally gas nitrated. |
|
|
|
|
|
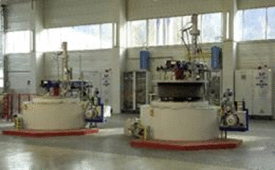
In our 2 shaft furnaces we perform heat treatments at a maximum temperature of 750 °C. These furnaces are primarily used for gas nitriding in ammonia gas stream, for nitro carburization, retrieval and tempering. |
|
|
|
|
|
These retort furnaces can be evacuated and are heated with natural gas. They are extended by a gassing system which sprays ammonia (NH3), nitrogen (N2) and carbon dioxide (CO2). |
|
|
|
|
|
There is an inlet for media like water, air and citric acid as well. |
|
|
|
|
|
Components will hardly show any tempering colors (during, for example, stress-relief annealing) due to the nitrogen atmosphere in the furnace. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|